Wei Yin 1,2,3†Yuxuan Che 1,2,3†Xinsheng Li 1,2,3Mingyu Li 1,2,3[ ... ]Chao Zuo 1,2,3,****
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Smart Computational Imaging Laboratory (SCILab), School of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
2 Smart Computational Imaging Research Institute (SCIRI) of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210019, China
3 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Spectral Imaging & Intelligent Sense, Nanjing 210094, China
4 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong SAR 999077, China
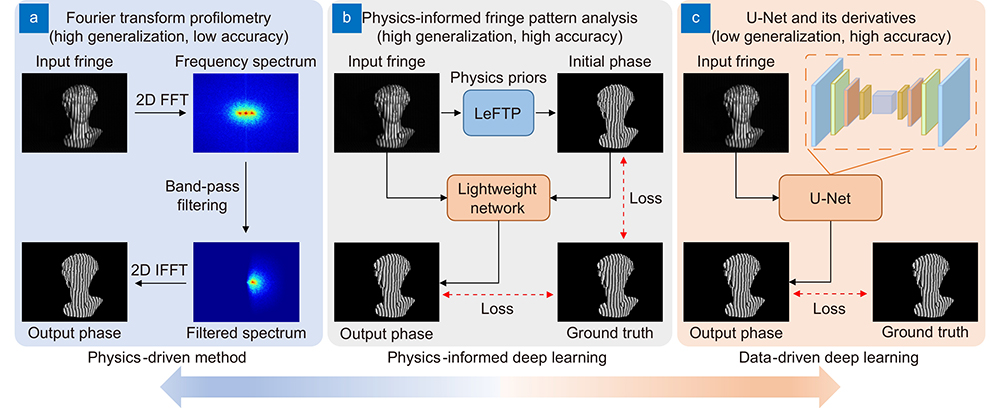
Recently, deep learning has yielded transformative success across optics and photonics, especially in optical metrology. Deep neural networks (DNNs) with a fully convolutional architecture (e.g., U-Net and its derivatives) have been widely implemented in an end-to-end manner to accomplish various optical metrology tasks, such as fringe denoising, phase unwrapping, and fringe analysis. However, the task of training a DNN to accurately identify an image-to-image transform from massive input and output data pairs seems at best na?ve, as the physical laws governing the image formation or other domain expertise pertaining to the measurement have not yet been fully exploited in current deep learning practice. To this end, we introduce a physics-informed deep learning method for fringe pattern analysis (PI-FPA) to overcome this limit by integrating a lightweight DNN with a learning-enhanced Fourier transform profilometry (LeFTP) module. By parameterizing conventional phase retrieval methods, the LeFTP module embeds the prior knowledge in the network structure and the loss function to directly provide reliable phase results for new types of samples, while circumventing the requirement of collecting a large amount of high-quality data in supervised learning methods. Guided by the initial phase from LeFTP, the phase recovery ability of the lightweight DNN is enhanced to further improve the phase accuracy at a low computational cost compared with existing end-to-end networks. Experimental results demonstrate that PI-FPA enables more accurate and computationally efficient single-shot phase retrieval, exhibiting its excellent generalization to various unseen objects during training. The proposed PI-FPA presents that challenging issues in optical metrology can be potentially overcome through the synergy of physics-priors-based traditional tools and data-driven learning approaches, opening new avenues to achieve fast and accurate single-shot 3D imaging.
optical metrology deep learning physics-informed neural networks fringe analysis phase retrieval Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230034
1 武汉理工大学理学院,湖北 武汉 430070
2 中兴通讯无线产品运营部,广东 深圳 518000
提出了一种少模光纤迈克尔孙干涉仪(MI)级联法布里-珀罗干涉仪(FPI)的游标增敏折射率传感器。少模光纤MI用作参考干涉仪,开放腔FPI作为传感干涉仪,解决了传统双FPI传感器的参考干涉仪制备复杂、可控性差的问题。仿真研究了单模-少模光纤错位量对少模光纤模式激发效率的影响,以及少模光纤长度对增敏倍数的影响。基于仿真优化参数制备了少模光纤MI-FPI传感器,并测试了其折射率响应特性,分析了增敏极限及限制因素。该传感器在1.3384~1.3412的折射率范围内的折射率灵敏度达到12466.956 nm/RIU(灵敏度单位),相对于无MI级联的单个FPI传感器提升了12.29倍,放大倍数可基于少模光纤长度灵活控制。该方法使传感器的增敏效果显著、增敏倍数可控、制备方法简单且光谱稳定性好,在折射率传感领域具有潜在的应用价值。
光纤光学 迈克尔孙干涉仪 少模光纤 模式反射 游标效应 折射率传感器 光学学报
2023, 43(19): 1906006
1 长春理工大学 光电工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
2 苏州联讯仪器股份有限公司设备部,江苏 苏州 215000
为了测试高速通信光模块在极端环境下的工作性能,并提升其出厂测试效率,设计了高速通信光模块热控系统。使用该系统不仅可以实现单独测试QSFP-DD封装模式的光模块,还可以实现双通道并行测试QSFP-28封装模式的光模块,成功使光模块测试效率提升一倍。首先,根据半导体制冷器的特性设计了待测试件热电制冷器组件,Flotherm的仿真结果表明热电制冷器组件可用。接着,根据半导体制冷器的原理及特性,设计了热排散系统。最后,将热控系统与水冷机的控温效率和效果做对比。实验结果表明:热控系统可以在110 s内实现光模块壳温在0~65 ℃之间的快速调控。热控系统基本满足对常用封装方式的高速通信光模块的控温需求,且相对于水冷机而言,具有小型化、低噪音、零震动的优势,更利于光模块集成化测试。
光纤通信 热控系统 热仿真 光模块 optical fiber communication thermal control system thermal simulation optical module 红外与激光工程
2023, 52(5): 20220705
尹维 1,2,3†李明雨 1,2,3†胡岩 1,2,3冯世杰 1,2,3[ ... ]左超 1,2,3,*
1 南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院智能计算成像实验室(SCILab),江苏 南京 210094
2 南京理工大学江苏省光谱成像与智能感知重点实验室,江苏 南京 210094
3 南京理工大学智能计算成像研究院(SCIRI),江苏 南京 210019
4 苏州亚博汉智能科技有限公司(Abham),江苏 苏州 215000
散斑投影轮廓术通过投影单幅随机散斑图案编码场景的深度信息,利用散斑匹配技术建立立体图像间的全局对应关系,从而实现单帧3D重建。但由于被测物体表面的复杂反射特性和双相机间存在的视角差异,投影单幅散斑图案无法为整个测量空间中每个像素编码全局唯一的特征,由此带来的误匹配问题导致测量精度较低,难以满足一些工业场景的高精度测量需求。提出一种基于垂直腔面发射激光器(VCSEL)投影阵列的散斑结构光三维成像技术及其传感器设计方法,所研制的三维结构光传感器集成了3个小型化散斑投影模组,投影一组空间位置不同的散斑图案,对被测场景的深度信息进行高效时空编码。提出一种由粗到精的时空散斑相关算法,以提升测量精度,重建复杂物体的精细轮廓。通过精度分析、三维模型扫描、小目标金属零件检测、复杂场景测量等实验证明,所提三维结构光传感器实现了远距离、大视场的高精度三维测量,可潜在应用于零件分拣、机器人码垛等工业场景。
三维成像 立体视觉 光学成像 散斑投影 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(8): 0811014
1 长春理工大学光电工程学院光学工程系,吉林 长春 130022
2 浙江大学现代光学仪器国家重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310027
提出一种反射型法布里-珀罗(FP)标准具和微环谐振腔级联的温度传感器。该温度传感器由光纤反射镜、FP标准具和微环谐振腔构成。利用强度探测的方法,仿真计算和实验验证表明,温度传感器具有较高的灵敏度和较低的探测极限。将宽带光源和滤波器组合作为实验的输入光源,反射型FP标准具起到滤波的作用,温度传感元件是微环谐振腔。仿真计算得出该温度传感器的灵敏度为2.1406 dB/℃。实验结果表明,该温度传感器的灵敏度为1.9434 dB/℃,探测极限为0.01 ℃。
传感器 光纤反射镜 法布里-珀罗标准具 微环谐振腔 强度探测 灵敏度 探测极限 光学学报
2022, 42(23): 2328002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optical Engineering, School of Opto-Electronic Engineering, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Centre for Integrated Optoelectronics, Department of Optical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
3 Jinan GK Medtech Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd., Jinan 250000, China
Based on the Vernier effect of the cascaded double ring resonator (CDRR) sensor, a sensor consisting of a microfluidic control system, a sensing ring, and a reference ring with a micro-heater for thermal tuning is proposed in this paper. In wavelength interrogation, a broadband spectrometer or a large tunable range laser is not required. The shift of the output spectrum caused by the refractive index change of the sample is converted into the change of the electric power by the thermal tuning heater. Due to the Vernier effect, the sensitivity of the sensor is 20 times higher than that of the single ring. The spectral envelope of the thermal-optic tuning of the sensor was fitted by a Gaussian function in the wavelength range of 8 nm. The experimental results showed that the sensitivity was 33.703 W/RIU, and the limit of detection was .
cascaded double ring optical resonators Vernier effect thermal-optic effect Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(1): 011301
航天工程大学 宇航科学与技术系 激光推进及其应用国家重点实验室,北京 101416
为研究不同金属材料的激光烧蚀推进性能,对常见的七种金属材料:Al,Fe,Ni,Cu,Y,Ag,Au,使用波长1 064 nm,脉宽8 ns的Nd:YAG激光器在大气下进行烧蚀,测量了烧蚀质量、冲量、冲量耦合系数、比冲和能量转化效率等推进性能参数,获得了激光功率密度对推进性能的影响规律。实验结果表明:相同激光功率密度下,Fe的烧蚀质量最大,Y的烧蚀质量最小;Al,Au,Cu的冲量较大,Ag的冲量最小;Au的冲量耦合系数和比冲均值在七种金属材料中最大,分别在激光功率密度为
$1.72 \times {10^{10}}\;{\rm{W}}/{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^2}$![]()
![]()
和
${{2}}{{.98}} \times {10^{10}}\;{\rm{W}}/{\rm{c}}{{\rm{m}}^2}$![]()
![]()
时达到40.7 μN/W和500 s的最大值,平均能量转化效率可达6%。
红外与激光工程
2021, 50(S2): 20210277
郑州航空工业管理学院材料学院, 郑州 450015
利用化学气相沉积(CVD)法, 以甲烷为碳源在管式炉中合成了单体石墨纤维(MGF)。选取长度为3.426 mm, 顶端球面半径为11.26 μm的单体石墨纤维直立于圆铜片上作为阴极, 以导电ITO玻璃作为阳极, 采用二极管结构在真空室中进行直流场发射测试, 证实MGF的开启场强为0.477 5 V/μm。基于有限元仿真软件ANSYS进行电磁场分析, 计算了MGF在不同电压下的有效发射面积。结果表明, 当电压为5.36 kV时, MGF达到最大发射面积为796.226 μm2, 在实验测量电压范围内, 平均发射电流密度可以达到46.069 A/cm2, 单体石墨纤维具有良好的场发射特性。
单体石墨纤维 场发射 有效发射面积 电流密度 场增强因子 monomer graphite fiber field emission effective emission area current density field enhancement factor
1 辽宁科技大学应用技术学院, 辽宁 鞍山, 114051
2 辽宁科技大学理学院, 辽宁 鞍山, 114051
本实验使用Nd: YAG激光焊接机对双相钢进行工艺研究, 分别选取了电流、脉宽、频率三组参数, 利用正交试验法分析焊接质量的影响, 对测量结果进行极差分析, 得到所选取的最佳参数依次为: 电流110 A, 频率14 Hz, 脉宽1.4 ms; 进行方差分析, 得到电流对焊接质量影响的显著性大于频率, 脉宽几乎没有影响。
激光焊接 正交法 双相钢 极差 laser welding dual-phase steel orthogonal experiment range